
How do interest rates affect your investments?
Last Updated on 26 January 2024 by Equipo Urbanitae
Since 2022, interest rates have been making numerous headlines. The return of inflation, a problem nearly forgotten for 14 years, has brought about significant changes in monetary policy worldwide. In this article, we explore what effect this has on our daily lives and, most importantly, how interest rates affect investments.
What are interest rates?
First and foremost, it’s important to clarify what interest rates are. In simple terms, interest rates are often referred to as the “price of money,” although this isn’t an exact definition. Indeed, interest is somewhat like a price, as it’s what we pay to a bank in exchange for them lending us money, as stated by the Banco de España. However, the interest rate is also what banks pay to their customers for depositing money with them.
In other words, interest rates determine what we pay to the bank when we take out a loan and what banks pay us to borrow our money in the form of a deposit. These rates are heavily influenced by the rates set by the central bank. In Spain and the rest of the European Union, this institution is the European Central Bank (ECB), whose primary objective is to maintain price stability, i.e., keep inflation in check. Yesterday, the ECB had its first meeting of 2024 and, as expected, kept the interest rates at 4.5%.
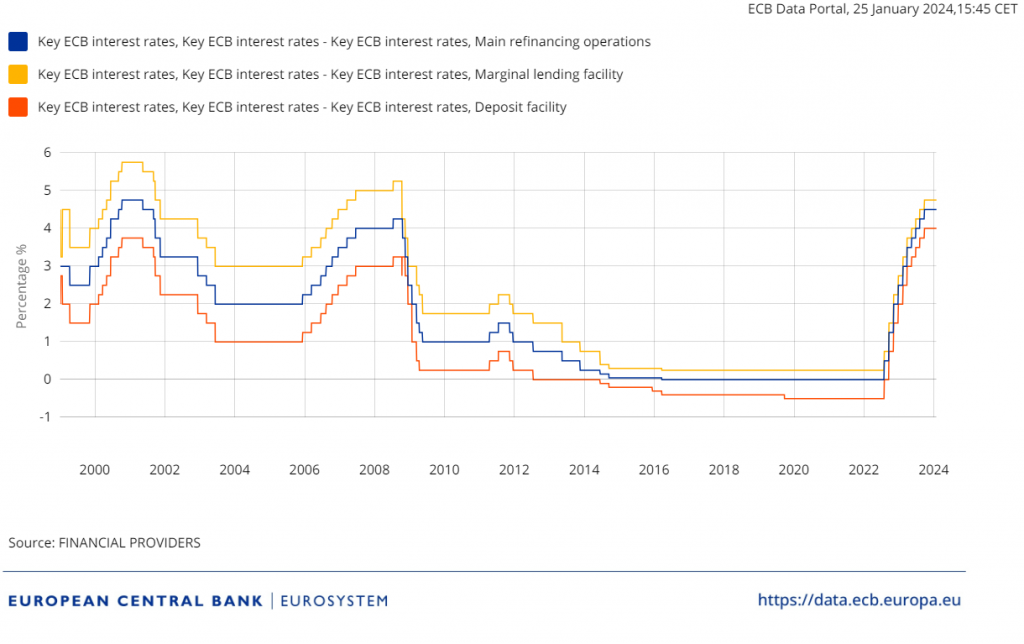
So, when the ECB raises the key rates (there are three), financing becomes more expensive. Banks have to pay more to borrow money from the ECB. Simultaneously, the central bank pays more to the banks that have deposited their money there. As access to financing becomes more costly and saving becomes more attractive, fewer loans are requested, overall demand in the economy decreases, and, in principle, inflation goes down.
How do interest rates affect investments?
Changes in interest rates don’t have immediate effects on the economy. Typically, it takes a few months for these effects to become apparent. However, markets do take note of monetary policy decisions as soon as they are known, and their consequences soon become evident. This is the case, for example, in stock markets.
In general, stock markets usually decline when interest rates rise. There’s less money available to spend, consumers buy less, and businesses feel the impact. However, some sectors typically benefit from interest rate hikes. Have you guessed it? Yes, banks usually improve their profits when interest rates rise because they can charge more for the money they lend.
Usually, stocks and bonds follow opposite trends. We’ve already seen that with high-interest rates, stocks suffer. What about bonds? It depends. New bonds, i.e., the debt securities issued in this environment of high-interest rates, become very attractive because they combine low risk and a higher interest rate precisely due to the rise in interest rates.
However, already-circulating bonds are penalized. Debt securities issued when interest rates were lower pay a less competitive interest, and therefore, their price will decrease.
What about alternative investments?
In the case of alternative investments, like commodities, when interest rates rise, commodity prices tend to fall. It is believed that an environment of higher rates is less favorable for investments in commodities, and vice versa.
In the real estate sector, the reality is more complex. On the one hand, as we’ve seen in Spain, mortgages are more expensive when interest rates rise. Consequently, fewer people can afford to access the financing needed to buy a house: the solvent demand for housing decreases. On the other hand, similar to already-circulating bonds, payments resulting from rents might be less competitive in a high-interest rate environment.
However, it all depends on the market. In Spain, for example, the main feature of the real estate market today is the lack of supply. Therefore, even though fewer mortgages have been signed, and real estate purchases have decreased, prices remain high. More houses are simply needed than are available. The same applies to rents, which have continued to rise, providing landlords with an inflation-resistant source of income.
In the case of Urbanitae, the answer is clear: real estate is an excellent store of value in times of inflation and high-interest rates. Despite uncertainty and rising construction costs, real estate crowdfunding has proven to be a haven for investments, combining a moderate level of risk and high returns— an average of 16% IRR in over 30 projects returned by Urbanitae to date.
In summary
The answer to how interest rates affect investments is not obvious. For most investors, it will depend on the composition of their investment portfolio. Generally, high-interest rates cause the prices of stocks and higher-risk assets, such as cryptocurrencies, to fall. Similarly, in an environment of high-interest rates, people usually prefer investments with lower risk, such as Treasury bills. Therefore, diversification is crucial to balance risks and achieve better long-term results.

